 Elena's Planet
Elena's Planet  Elena's Planet
Elena's Planet Angiosperms are flowering plants. They are the largest and most diverse group within the Plantae kingdom, with over 300,000 known extant species. This page will go over some of the numerous families of angiosperms. You will likely see many plants you recognize in this list. Before we jump in, take a look at this phylogeny of flowering plants by so you can see how the major clades in discussion relate to each other
Please note that this is not a comprehensive list of all angiosperms, that would be sooooooo long! I included the most prominent families that are relevant both in taxonomy and in human cultivation, with a clear bias towards Floridian plants.
Note: this page has a lot of images, so sections are disabled by default. It is not reccomended to enable multiple sections over a cellular network.
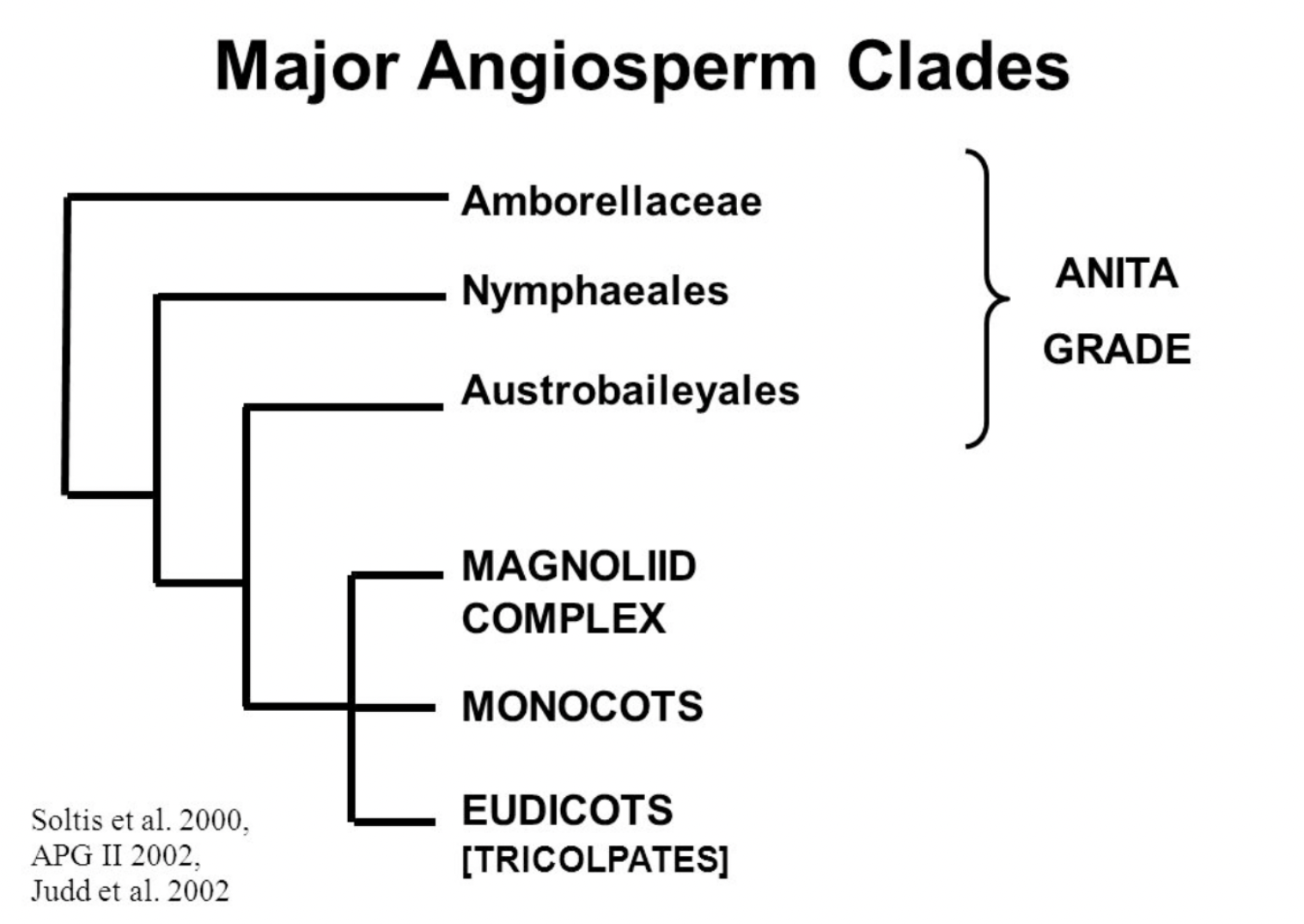
ANITA grade angiosperms are the most primitive angiosperms. They are of particular interest to plant taxonomists because they help us imagine the evolutionary transition between gymnosperms and angiosperms.
| Name | Common Name/Examples | Notable feature(s) | Botany | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amborellaceae | Amborella | New molecular data shows this may be the earliest angiosperm in evolutionary history | Leaves are two-ranked with distinctly rippled/serrated margins. Contains only tracheids, vessels are absent. Small white inflorescences |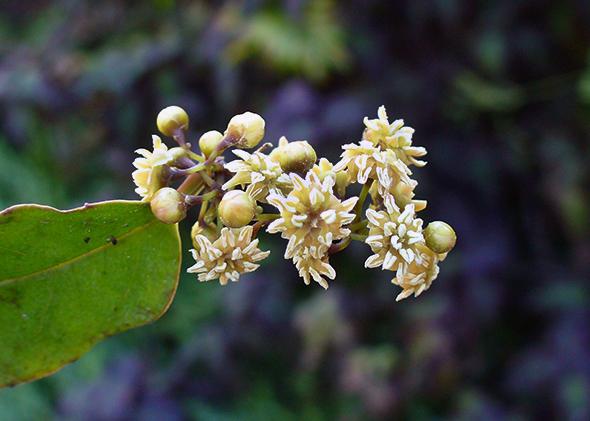  Source |
| Nymphaceae | Water Lillies | Aquatic plants with flat leaf blades floating on the surface | Plants aquatic, rhizomes anchored in muck in still water Leaves margins entire Flowers often showy, numerous parts, rising above surface of water Our native water lily in Florida is the Spatterdock! |
 Source |
| Austrobaileyales | Star Anise | Lack differentiation between inner and outer floral whorls | This one ends in “ales” and not “aceae” because it is an order, not a family Debated whether or not it has separate families inside, so the entire order is treated as one unit when discussing ANITA grade Often beetle-pollinated |
 Source |
The Magnoliids have evolved characteristics that are not present in the primitive ANITA grade flowers, but they are neither monocots nor dicots. The group can be categorized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and leaves with branching veins.
| Name | Common Name/Examples | Notable feature(s) | Botany | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnoliaceae | Magnolia | Trees with large, singly borne flowers and waxy leaves | Flowers with numerous spirally arranged organs On a long and tapered receptacle Stamens rapidly fall off |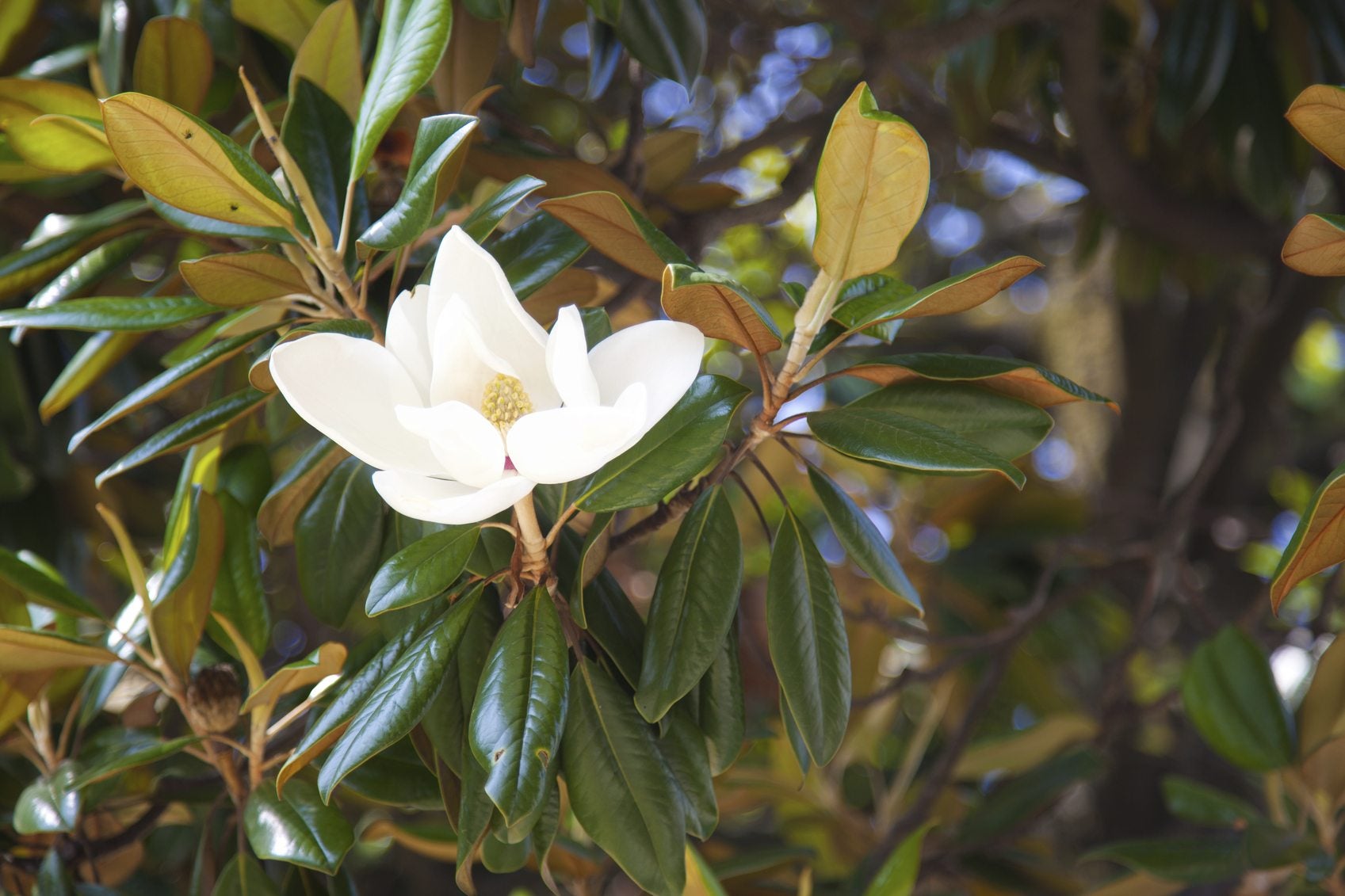  Source |
| Annonaceae | Paw Paws Custard Apples | Fruit a paw paw- large and fleshy with few large seeds Source | Small trees or shrubs Flowers trimerous Single and with fleshy perianth members |
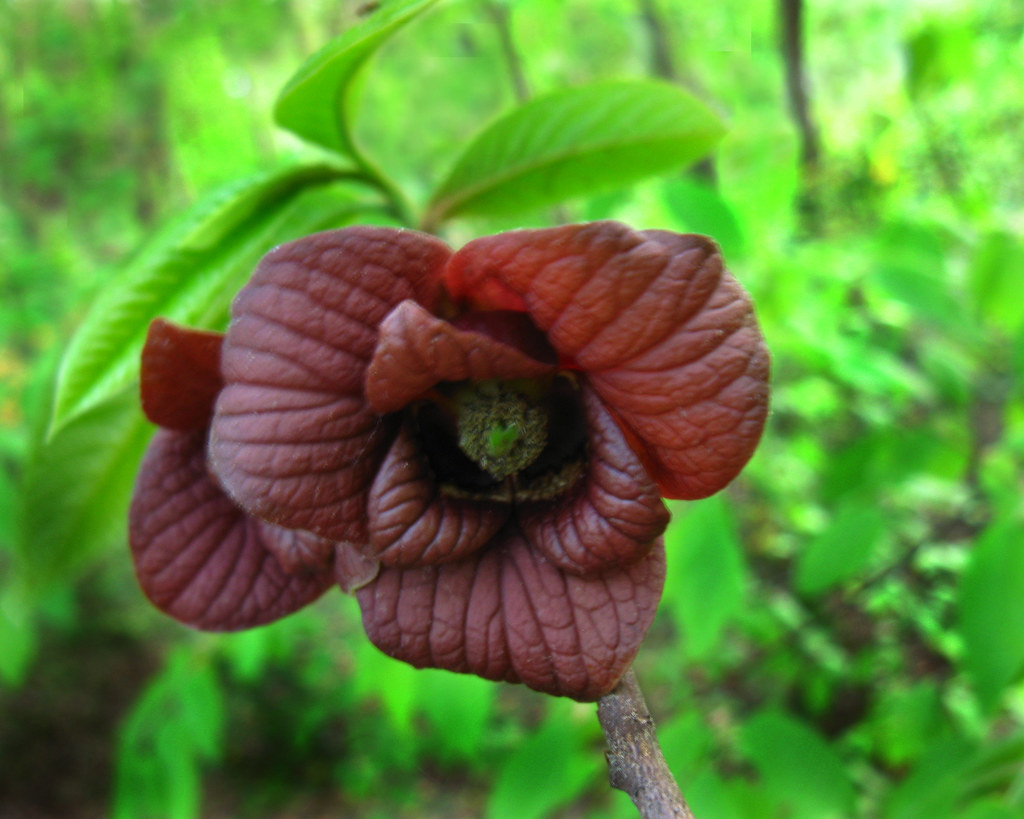 Source |
| Calycanthaceae | Sweetshrubs Spicebush | Single maroon flowers with numerous free petals | Only 10 known species, one can be found in SE USA Receptacle elongated |
 Source |
| Lauraceae (Note: This family is considered a dicot by many taxonomists, but it still is recognized as part of the magnoliid clade, so it deserves a spot here too.) | Laurels Sassafras Cinnamon Avocado | Trees or shrubs with simple leaves and aromatic compounds | Flowers small and in inflorescences Sassafras has leaves with 3 different shapes on the same individual |
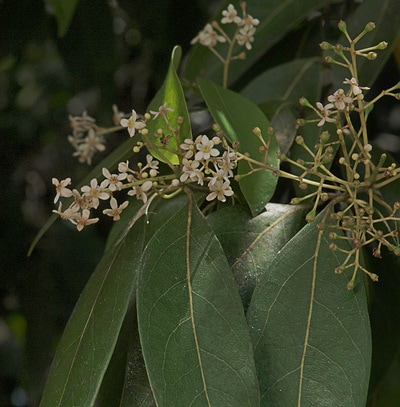 Source |
| Aristolochiaceae | Birthwort | Bizarrely shaped flowers, tubular at base and fleshy | Ant and beetle pollinated Rosettes with deep green, glossy leaves Flowers brown to maroon, often with short pedicels leaving them at ground height |
 Source |
With magnolids and ANITA grade out of the way, now we can focus on the two largest clades of flowering plants, monocots and dicots! If you don't know, "cot" is is short for "cotyledon" (i.e. an embryo leaf) so the main difference is, does the plant pop out of the ground with one leaf or two leaves? There are some other differences as well but the cotyledon is the main difference, and the one that these groups were named after
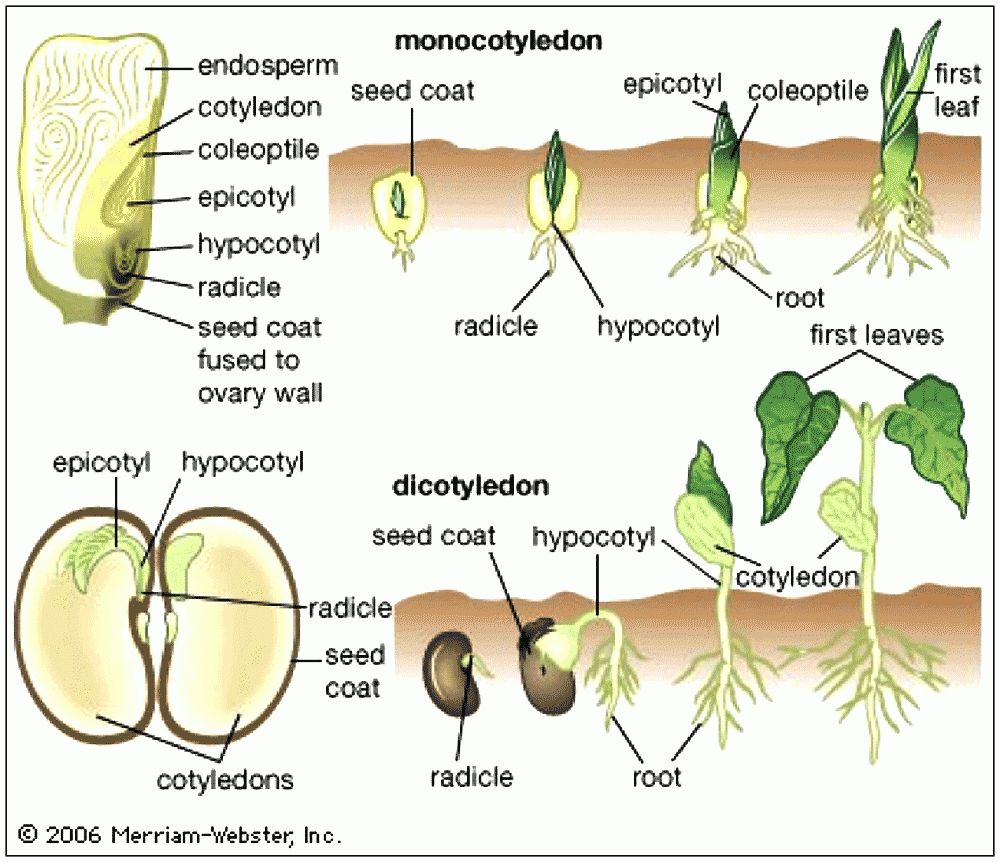 Source |  Source |
| Name | Common Name/Examples | Notable feature(s) | Botany | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Araceae | Arums Peace Lily | Contains a SPADIX, a tightly packed inflorescence subended by a SPATHE (modified leaf) | Flowers unisexual, usually segregated on spadix Some varieties can generate heat Perennial Plants |
 Source |
| Lemnaceae (Note: Gets moved in and out of araceae) | Duckweed | Floating aquatic, looks like little green dots | World record for smallest flower Sometimes has spadix, but often reproduces vegetatively Flowers are microscopic |
 Source |
| Alismataceae | Water Plantains | Grows in wet conditions, loose inflorescences | Actinomorphic flowers Three white petals and numerous stamens Sepals not part of the showy perianth Large erect leaves |
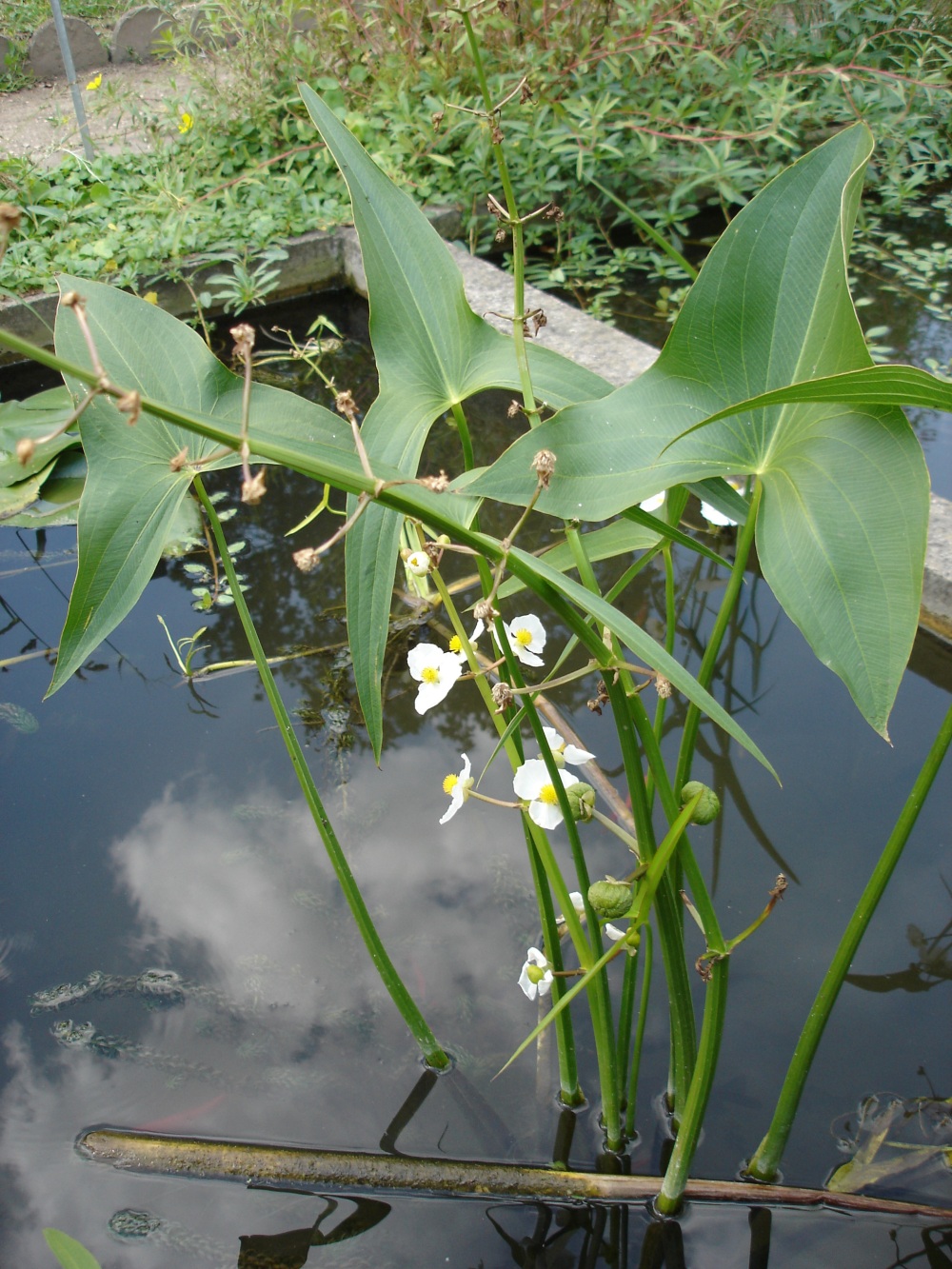 Source |
| Name | Common Name/Examples | Notable feature(s) | Botany | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lilaceae | Lillies | Showy flower with 3 sepals and 3 petals Ovary with 3 fused carpels | Flowers bisexual and actinomorphic Leaves usually linear |
 Source |
| Smilaceae | Smilax | Vines, usually prickly Unique leaf shape | Broad, alternate leaves with parallel venation Flowers small, white, and unisexual and actinomorphic |
 Source |
| Iridaceae | Irises | Showy, actinomorphic flowers 3 petals and 3 sepals (often looks like 6 petals) and grass-like leaves | Erect petals and relaxed sepals Petaloid style Leaves often folded |
 Source |
| Orchidaceae | Orchids | Stamens and style fused into a column. One large lower petal called a lip | Zygomorphic flowers Sepals often petaloid Two-ranked leaves |  Source |
| Dioscoreaceae | Yams | Perennials, usually vines. Heart shaped leaves and often root tubers | Simple, broad, alternate leaves Net-veined Flowers in clusters borne from leaf axils |
 Source |
| Arecaceae | Palm trees | Erect, unbranching woody stem with large plicate leaves | Leaves often compound Inflorescences Fruit a one-seeded drupe or berry If branched, dichotomous |  Source |
| Commelinaceae | Dayflowers Spiderworts | Sheathing leaves, succulent stems. | Stamens in two whorls of three Often blue flowers Bisexual flowers Varying symmetry |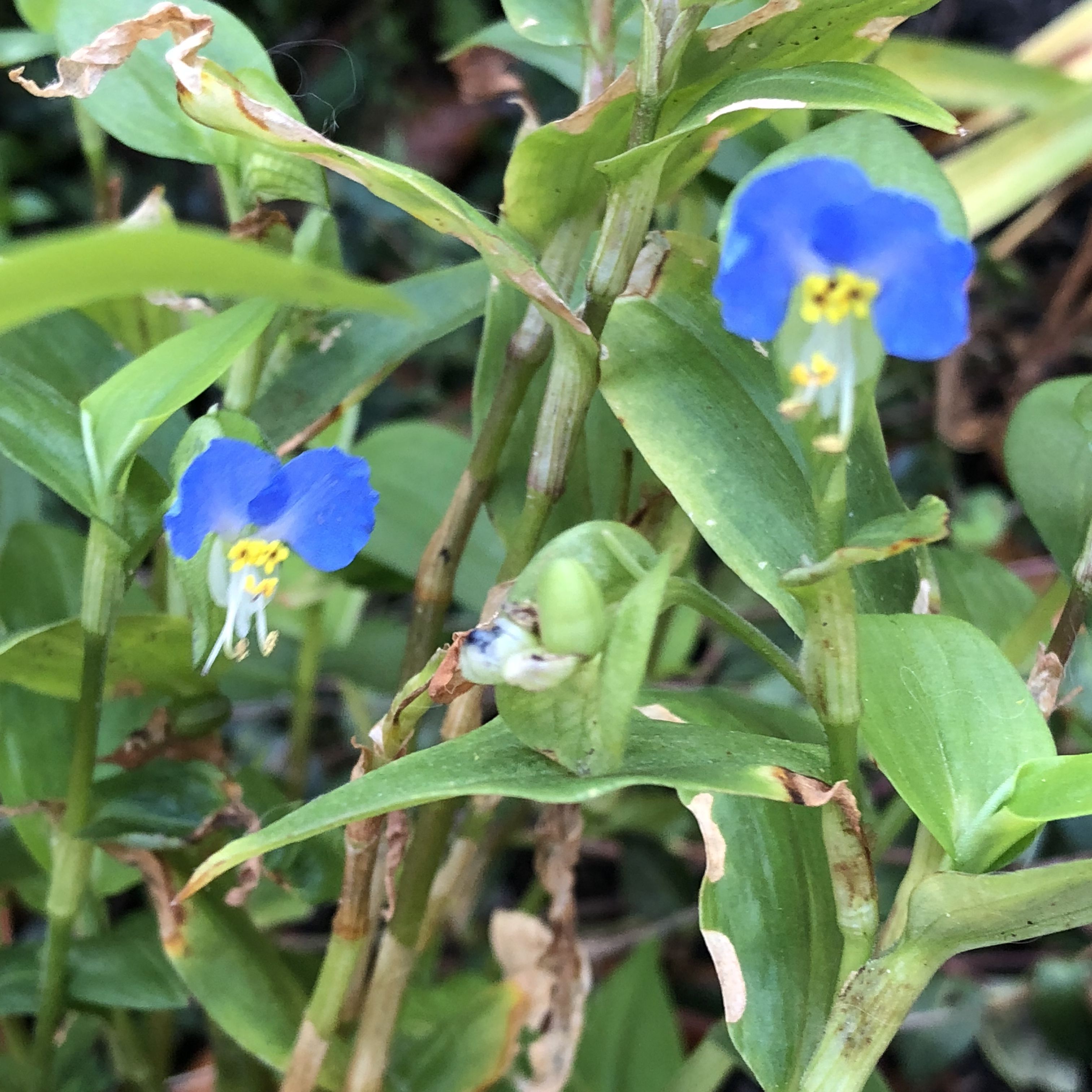  Source |
| Pontederidaceae | Pickerel Weed | Submerged, floating, or root emergent aquatic with purple racemes | Flowers bisexual and slightly zygomorphic Annual or perennial herbs |  Source |
| Bromeliaceae | Bromeliads Air Plants Pineapple | Overlapping spirally arranged leaves that form a "cup" | Often epiphytic but not always Some varieties have lots of peltate or stellate trichomes that give a silvery appearance Flowers bisexual, usually showy with colorful bracts |  Source |
| Typhaceae | Cattails | Inflorescence a dense cylindrical brown spike Divided into male flowers (above and deciduous) and female flowers (below and persistent) | Grass-like leaves Perennial, grow in wet places |  Source |
| Eriocaulaceae | Hatpins Pigworts | Flowers packed into tight circular inflorescence, usually white | Basal, grass like leaves Flowers unisexual Found in wetlands, savannas, or pine forests |  Source |
| Xyridaceae | Yellow Eyed Grasses | 3-merous yellow flowers emerging from a "cone" | Basal, grass-like leaves Flowers are delicate and ephemeral |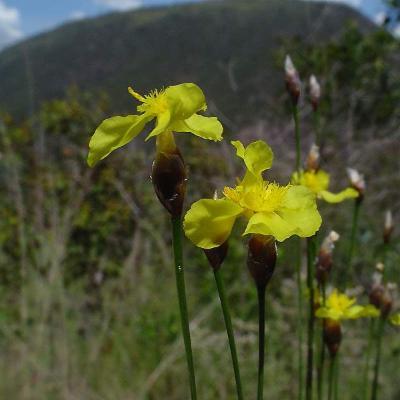  Source |
| Juncaceae Graminoid | Rushes | Grass like, but with hollow stems and brown inflorescence | Tufted herbs, can be found in boggy habitats Flowers bisexual and actinomorphic, with 3 sepals and 3 petals Leaves sometimes reduced to basal sheath |  Source |
| Cyperaceae Graminoid | Sedges | Linear grass-like leaves, but with no ligule and a triangular stem | Flowers bisexual or unisexual Perianth reduced to scales or bristles, if not completely absent |  Source |
| Poaceae Graminoid | Grasses Wheat Barley | Linear, alternate leaves with a ligule at base Source | Flowers tightly packed in spikelets Each small flower has 2 bracts outer=lemma inner=palea |  Source |
| Zingiberaceae | Ginger Caramom Turmeric | Rhizomatic herbs with aromatic, often spicy compounds | Alternate, two ranked leaves 3 petals and sepals 2 stamens and 4 staminodes, with 2 of them large and connate forming a "lip" Flowers bisexual, zygomorphic, and ephemeral |  Source |
| Cannaceae | Canna Canna Lily | Rhizomatic herbs. 3 sepals, 3 petals,1 stamen, and 3-4 petaloid staminodes | Leaves alternate, two ranked, or spiral Flowers bisexual, ephemeral, and asymmetrical |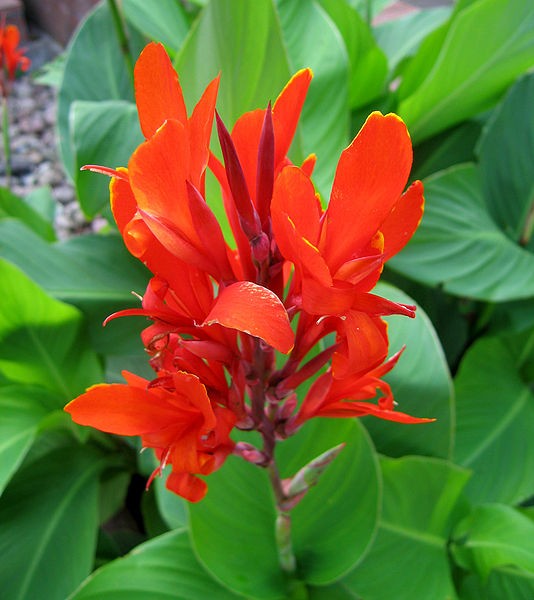  Source |
WIP, stay tuned!
| Ranunculaceae | Buttercups | Usually 5 petals, 5 green sepals, and numerous stamens | Includes Anemone Bisexual and radial |  Source |
| Berberidaceae | Barberries | Anthers dehiscing by flaps | Biseriate stamens 6 sepals and 6 petals |  Source |
| Papaveraceae | Poppy | Papery thin petals, crumbled in bud Milky sap | Sepals deciduous Numerous stamens Bisexual and radial flowers |  Source |
| Fumiaraceae | Fumewort Bleeding Hearts | Everything that papaveraceae has, except zygomorphic | Gets moved in and out of papaveraceae by taxonomists... Flowers usually also pendant |  Source |
| Caryophyllaceae | Carnation | Petals have a zig-zag "pinked" edge (named after pinking scissors) | Leaves opposite at swollen nodes 5 petals, sometimes deeply lobed and appear to be 10 petals Leaves often narrow and linear |  Source |
| Phytolaccaceae | Pokeweed | Pink to purple stems, dark purple berries | Leaves simple and alternate Flowers small, actinomorphic, 5-merous, and bisexual |  Source |
| Amaranthaceae | Amaranth | Inflorescences are determinate, terminal, or axillary | Leaves simple, variously attatched Flowers bisexual, very small and many |  Source |
| Portulacaceae | Purslane | Succulent herb, radial and bisexual flowers | Leaves simple Variously attatched leaves |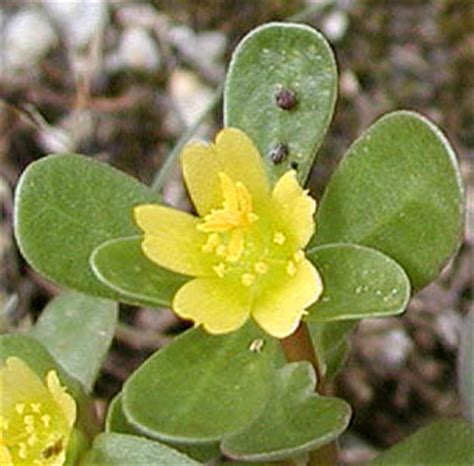  Source |
| Cactaceae | Cacti | Leaves reduced to spines Stems enlarged and fleshy, storing water | Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, with many perianth parts and stamens Ovary inferior |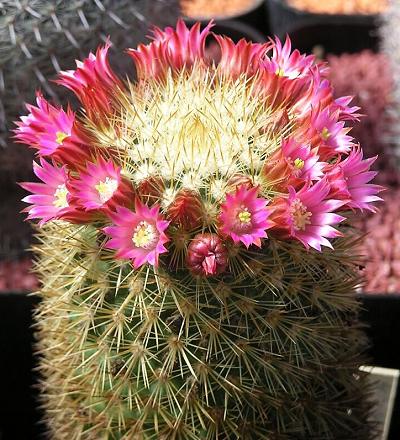  Source |
| Droseraceae | Sundew | Leaves covered in sticky glandular hairs that catch insects | Small, found in moist habitats Leaves spatulate to elongate in basal rosettes Flowers small and 5-merous |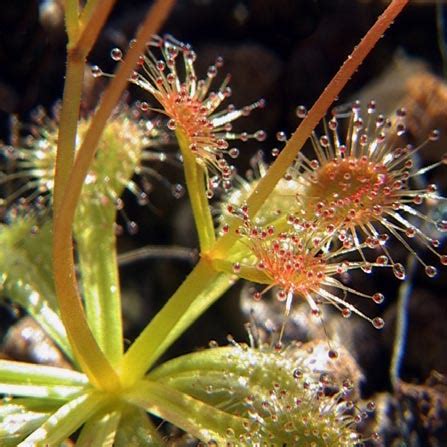  Source |
| Polygonaceae | Buckwheat | Ochrea at leaf nodes Source |  Source | |
| Saxifragaceae | Saxifrage | Leaves alternate and in basal rosettes | Flowers 5-merous, bisexual, and actimorphic Perigynous |  Source |
| Crassulaceae | Stonecrop Succulents | CAM (Crassulean Acid Metabolism) Photosynthesis | Leaves often simple, variously arranged Flowers bisexual and radial Ovary superior Sepals and petals 4 or 5 Each carpel subended by a scale-like nectariferous gland |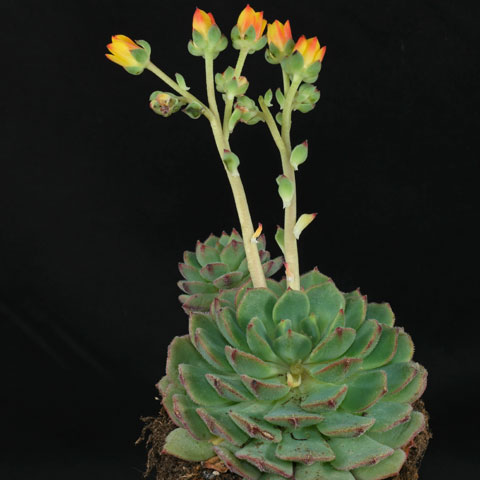  Source |
| Hamamelidaceae | Witch Hazel | Petals often long and "strap shaped" | Leaves simple, alternate, and often 2-ranked Flowers bisexual or unisexual Petals and sepals 4-5 |  Source |
| Altingiaceae | Sweet gum | Leaves often palmately lope Globose multiple fruit | Flowers unisexual, distributed on male (staminate) and female (carpellate) inflorescences that can be found on the same plant Shrubs and trees |  Source |
| Geraniaceae | Geranium | Fruit with elastic dehiscent schizocarps that curl on the beak | Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, and 5-merous (although many cultivars were bred to have more petals) Leaves alternate or opposite, with paired stipules Sometimes aromatic |  Source |
| Oxalidaceae | Wood Sorrel | Presence of oxalic acid Leaves often appear like shamrocks | Leaves alternate and compound Flowers bisexual and actinomorphic, 5 merous |  Source |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorb Spurge | Flowers grouped in specialized inflorescences called cyathia | Often with milky sap Leaves mostly alternate Includes poinsettias |  Source |
| Passifloraceae | Passionflower | A corona of thread-like filaments are present inside perianth | Leaves alternate, entire, or lobed Flowers actinomorphic and bisexual with a distinct configuration. |  Source |
| Fabaceae | Legumes | Fruit is a legume Three subfamilies | FABOIDEAE/ PAPILIONIDAE: Flowers strongly zygomorphic and bisexual, 5-merous, papilionoid MIMOSIDAE: Flowers actinomorphic and bisexual, perianth reduced, stamens very long CAESALPINOIDAE: Flowers actinomorphic to weakly zygomorphic, petals held open |  Source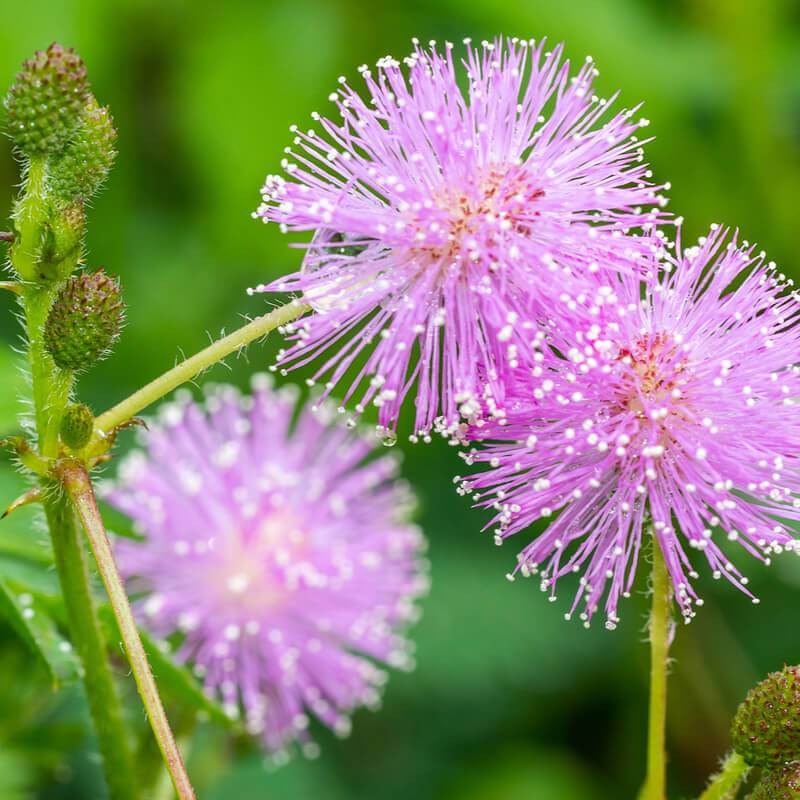  Source  Source |
| Rosaceae | Roses | Leaves with paired stipules | Flowers naturally 5-merous, but many cultivars bred to have more petals Flowers actinomorphic and bisexual A hypanthium is often present but not always |  Source |
| Urticaceae | Nettles | Trichomes ("urticaceous hairs") that are mineralized, sting like tiny shard of glass | Leaves alternate and spiral, OR 2-ranked and opposite Weedy herbs |  Source |
| Fagaceae | Beech Oak | Staminate flowers in pendulous cymes Carpellate flowers in clusters of 1-3 with acorn caps | Leaves usually simple and spiral Often lobed leaves Flowers unisexual, plants monoecious |  Source |
| Melastomataceae | Melastomes | Leaves with multiple midveins |  Source | |
| Onagraceeae | Evening Primrose | Hypanthium, ovary inferior, often 4-merous flowers | Leaves alternate or oppostie Flowers actinomorphic, bisexual, and usually 4-merous |  Source |
| Brassicaceae | Mustard Cruciferous vegetables | 4 petals, 4 sepals, and 6 stamens | Flower small and bisexual, usually more or less actinomorphic Fruit a silique or silicie Leaves alternate and simple, often disected |  Source |
| Malvaceae | Mallows | Filaments united into a tube or column that surrounds the style | Herbs and shrubs, rarely small trees Leaves simple, alternate, and with stipules Flowers actinomorphic, sepals 3 or 5, corolla of 5 valvate petals |  Source |
| Anacardiaceae | Sumac Cashew | Stamens inserted beneath a disc surrounding the ovary | Leaves alternate, simple or compound Flower small, bisexual/unisexual, and actinomorphic includes poison ivy |  Source |
| Ericaceae | Heath | Urn Shaped flowers | Corollas often campanulate or urceolate Flower bisexual and actinomorphic Petals fused into a corolla tube with free lobes Stamens often twice as many as corolla lobes Anthers open by apical pores |  Source |
| Sarraceniaceae | Pitcher Plants | Insectivorous Leaves tubular and vase-like | Flowers solitary Flower bisexual and actinomorphic Perianth and style usually tough and persistent |  Source |
| Solanaceae | Nightshade Peppers Tomatoes Eggplant | Flowers 5-merous, petals reflexed | Actinomorphic and bisexual Anthers usually stick together with the style just protruding Alternate leaves with no stipules |  Source |
| Convulvulaceae | Morning Glory | Corolla united into a trumpet shape tube that "untwists" as it opens | Climbing vines, herbs, shrubs, or trees Flowers 5-merous, actinomorphic, bisexual, and showy Leaves alternate and simple |  Source |
| Apocynaceae | Dogbane Milkweed | Corolla lobes overlapping in a rotating manner in bud | Leaves opposite or whorled 5 united sepals, 5 united petals Often with milky sap |  Source |
| Rubiaceae | Madder Coffee | Inferior ovary and reduced sepals | Leaves opposite or whorled with stipules Flowers 4, 5, or 6 merous. Actinomorphic and bisexual |  Source |
| Scrophulariaceae | Pigwort | Zygomorphic, often two-lipped | Flowers 5-merous Simple leaves alternate, opposite, or whorled. |  Source |
| Lamiaceae | Mint | Glandular hairs that release aromatic compounds Square stem | Opposite leaves in pairs that are perpendicular to each other Flowers zygomorphic |  Source |
| Apiaceae | Carrots Parsley | Flowers in simple or compound umbels | Leaves usually highly disected Often aromatic |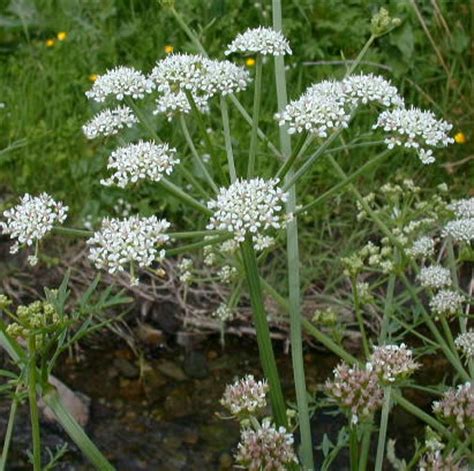  Source |
| Asteraceae | Sunflowers Daisies | Flowers in involucrate heads Reduced or absent sepal homolog (pappus) | Flowers usually 5-merous, actinomorphic, or zygomorphic Bisexual or unisexual Inferior ovary |  Source |